The digital marketing world is flooded with jargon and niche terminology that can be daunting for marketing novices.
For example, given the importance of link building in search engine optimization, users will likely encounter various types of links in their SEO journey.
The question is: How can a marketer devise a solid link-building masterplan or internal linking strategy if they don’t truly understand these terminologies in the first place?
In this resource, LinkStorm aims to illuminate internal vs. external links and uncover all types of links important for SEO.
What are Internal and External Links?
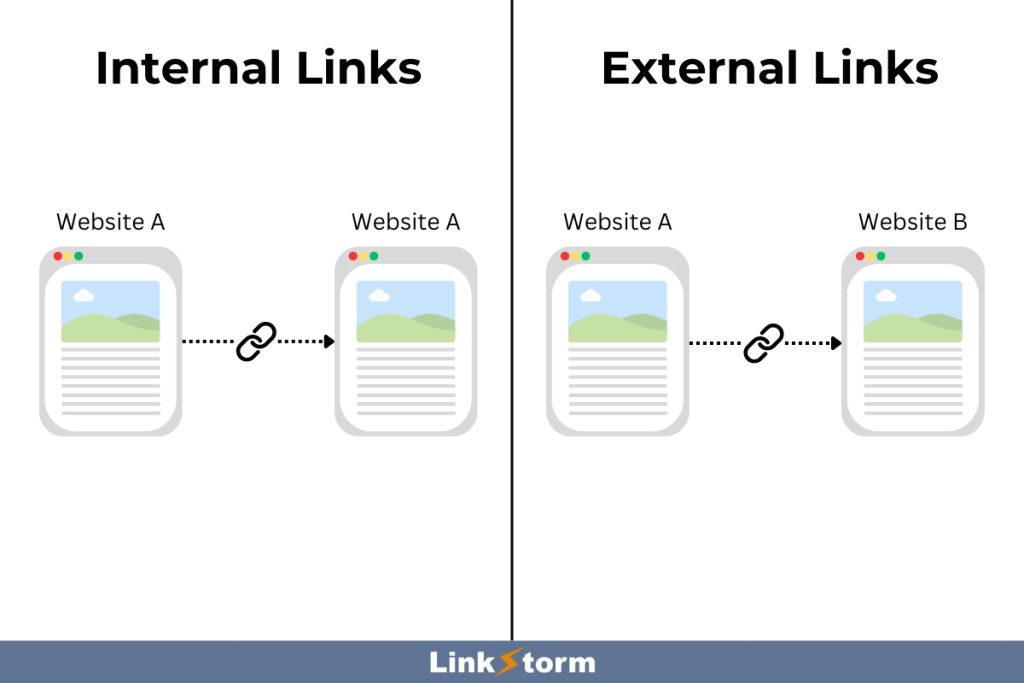
What are Internal Links?
Internal links are hyperlinks that take users from one page to another page on your website. These links help search engines like Google understand a website’s organizational structure and hierarchy.
Moreover, internal links also lead users to important pages relevant to their search journey. Strategically placing internal links can enhance a user’s experience and potentially boost a site’s search rankings.
Related: The Complete Guide to Internal Linking
What are External Links?
External links direct users from one web page to another on a different website. They are essential for providing additional information, supporting claims, or connecting related content across the web.
Linking externally might seem counterintuitive since you want to keep users glued to your website. However, external links improve a web page’s trustworthiness and accessibility by offering readers diverse perspectives and authoritative resources.
Internal Links vs External Links: A Toe-to-toe Comparison
External and internal links are clearly different by definition. However, this distinction is just the tip of the iceberg. If we investigate closely, we’ll uncover many differences between internal and external links.
We’ll take a look into five categories to differentiate internal vs. external links:
Purpose
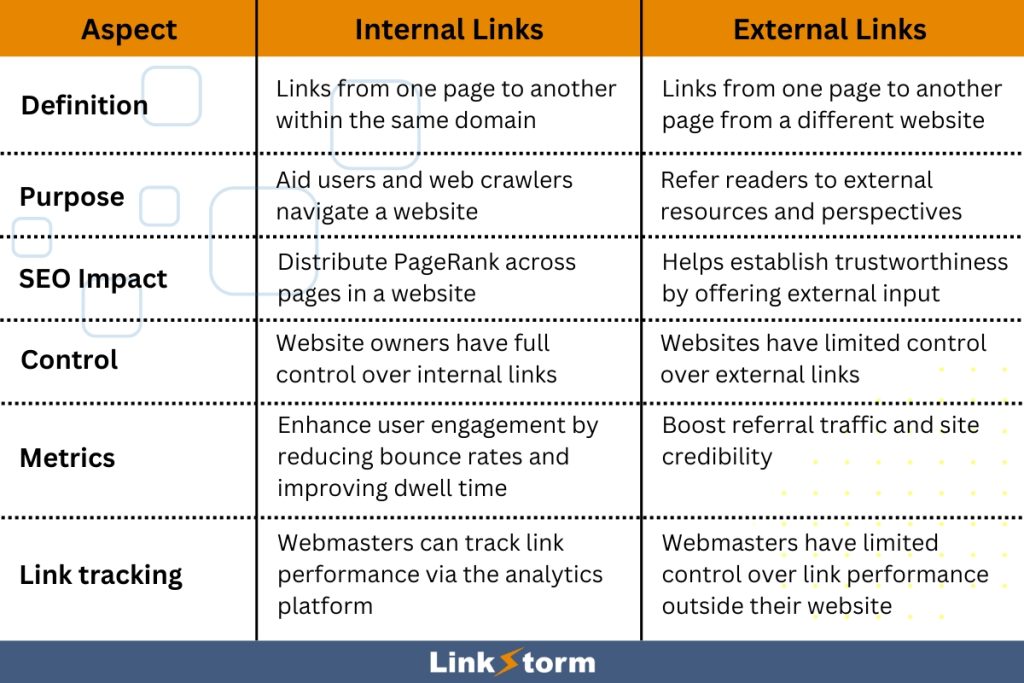
Internal links primarily guide users and web crawlers within a website’s ecosystem, facilitating navigation between pages or sections. They are placed to enhance user experience, promote the discovery of related content, and reinforce the website’s hierarchical structure.
In contrast, external links are intended to provide additional resources, references, or supporting evidence from other websites or domains. They expand the breadth of information available to users, offering diverse perspectives and enriching the content with external insights and authority.
SEO Impact
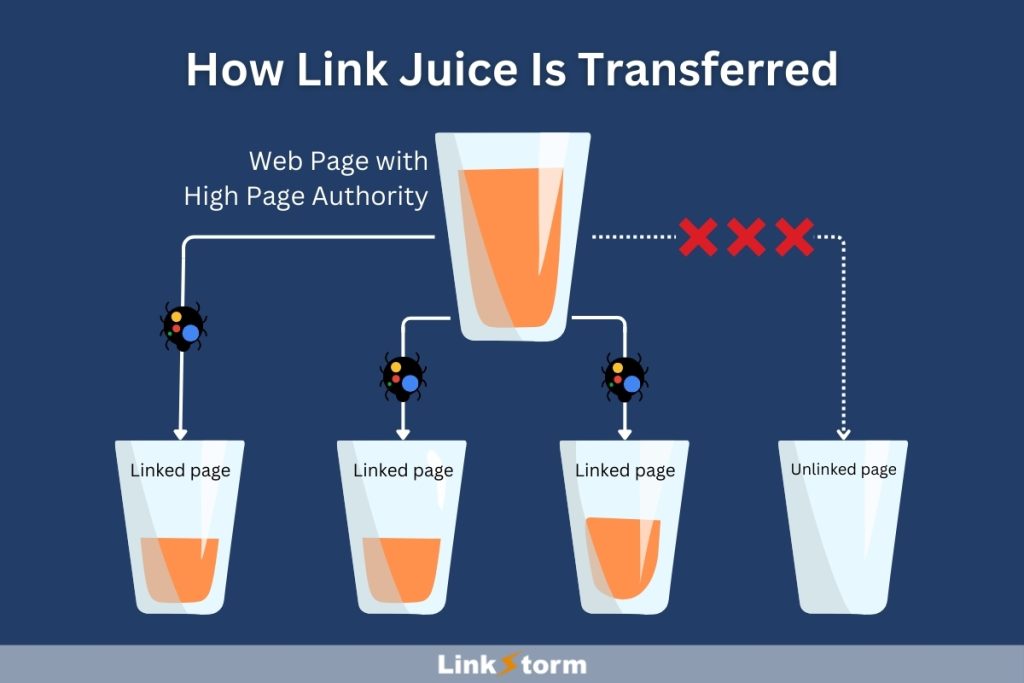
Like other link-building practices, internal links pass link juice from the source to the linked page.
Internal links boost a website’s SEO by distributing PageRank across pages, aiding the visibility of important pages on SERPs. They also play a crucial role in improving website crawlability and indexation by search engines, supporting improved SEO performance.
External links, on the other hand, do not directly benefit the SEO of the source site. If anything, outbound links count as backlinks for external authoritative sites, improving the linked site’s SEO performance.
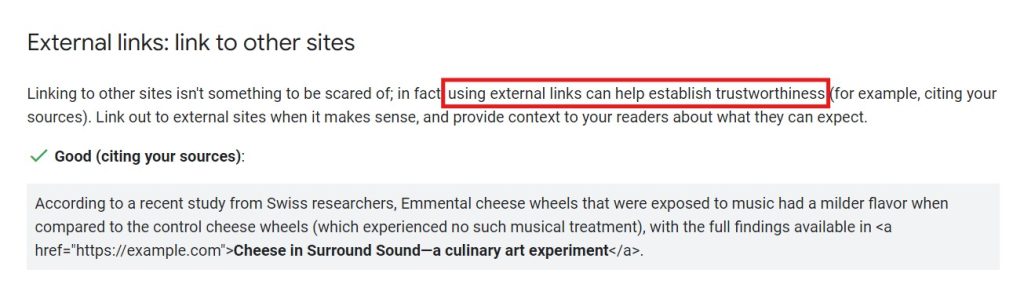
However, external links also have some SEO merits. According to Google, it helps establish the site’s trustworthiness, which gains the trust of search engines.
Control
Internal links give website owners complete control over the internal linking structure within their domain. This allows them to maneuver their links strategically, prioritizing important pages and guiding user navigation. Webmasters can adjust internal links to optimize user experience, promote key content, and facilitate content organization.
With external links, web owners have limited control as they link to relevant pages hosted on other domains. While they can choose which external sources to link to, they cannot control the content or the availability of those external pages. In other words, web owners are vulnerable to broken links or content changes beyond their control.
This lack of control over external links poses risks regarding the reliability and consistency of the linked information. As such, website owners must carefully vet external sources before linking.
Metrics
Internal links contribute to on-page engagement metrics by guiding users to explore more pages within the same website. This helps reduce bounce rates and increase average session duration or dwell time. Internal links also improve traffic value since they are useful in directing users to important pages, like landing pages and conversion funnels.
In contrast, external links influence off-site metrics. These outbound links contribute to referral traffic metrics as users click the links to access external resources. Moreover, indiscriminate external linking may also reduce readers’ time-on-site, as these links take users outside of the domain.
Link Tracking
Web owners can track internal link performance within the site’s analytics platform, such as user behavior, navigation patterns, and click-through rates. This allows users to optimize site structure, benefit user experience, and identify content/conversion optimization opportunities.
However, website owners have limited control over the metrics related to outbound links. Even with tools, tracking user behavior on external websites can be challenging.
While website owners can track the number of clicks on external links using tools like UTM parameters or specialized tracking software, they have limited visibility into user behavior once users leave their website.
Here is a tabularized breakdown of external links vs internal links:
Importance of Internal Links and External Links for SEO
Internal and external links have different objectives on a website. They also pose distinctive benefits when integrated into your overall SEO strategy. Here’s a quick run-through:
Benefits of Internal Links for SEO
1. Improved User Navigation
Internal linking enhances users’ search journey by guiding them to relevant content within the same website. This streamlines the exploration and discovery of valuable information for their inquiry. Well-placed contextual links also lower bounce rates by keeping users engaged with the content longer.
LinkStorm is an internal linking software designed to aid webmasters in building contextually pertinent internal links between relevant pages. The tool’s Opportunities tab provides users with untapped internal linking opportunities throughout their website.
Users can choose between two algorithms to find your internal links:
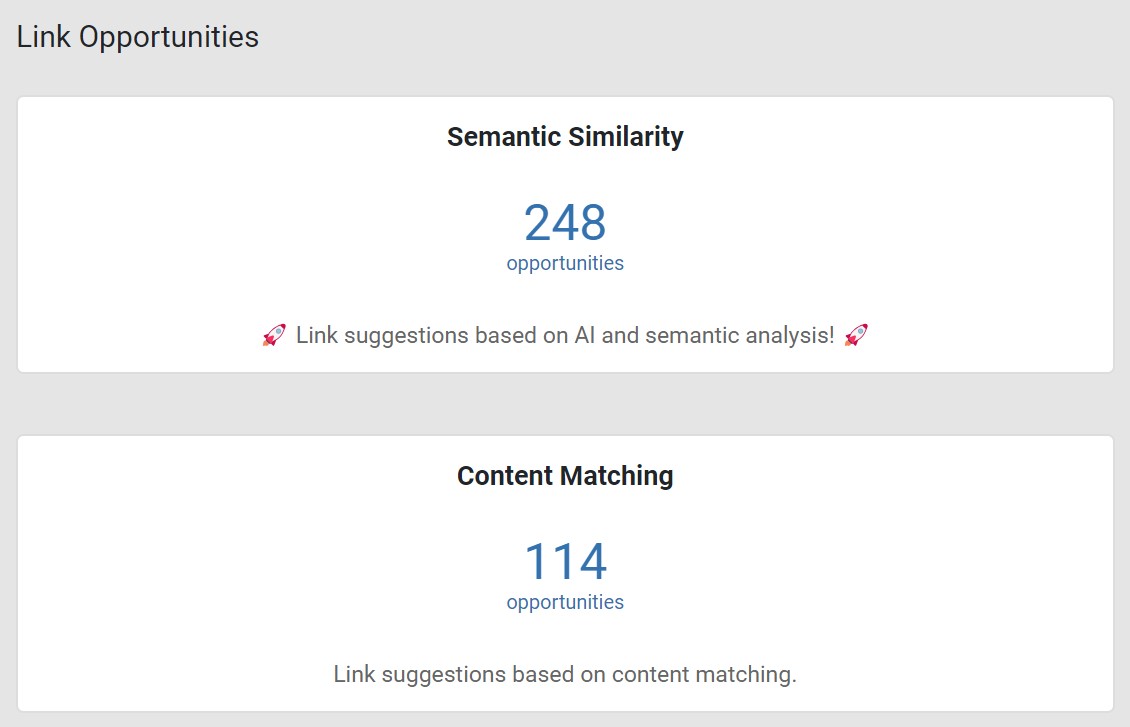
Semantic Similarity: Uses AI machine learning to suggest viable internal links to related web pages based on semantic analysis
Content matching: Uses seed keywords within the content as anchor text placeholders for internal link suggestions
You can then assess the feasibility of the tool’s internal link opportunities on your website and implement those suggestions accordingly via your site’s CMS dashboard.
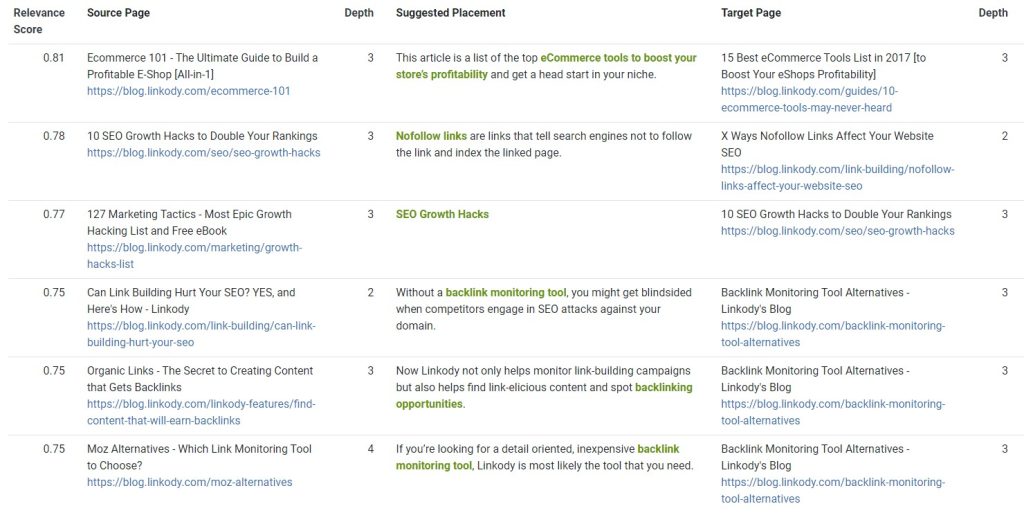
Here is an example of internal link suggestions on LinkStorm:
2. Enhanced SEO Performance
Internal links pass PageRank or link equity from the source page to the linked page. Strategic internal linking allows webmasters to control the direction of PageRank and enhance the page authority of specific web pages.
Users may take two approaches when controlling the direction of internal links:
- Scale-up approach: Directional internal linking where the PageRank is transferred from high-PA pages to fellow high-PA pages. This approach gives an additional boost to the SERP ranking of already favorably performing web pages.
- Scale-down approach: directional internal linking where the PageRank is transferred from high-PA to low-PA pages. This approach benefits poorly performing web pages on your site by transferring some authority from high-ranking pages.
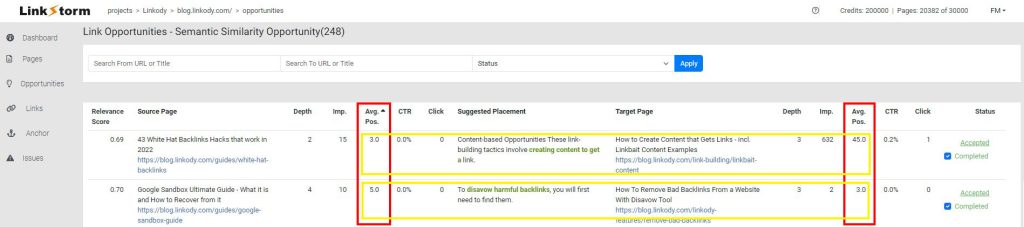
At LinkStorm, this can be achieved by enabling the GSC data toggle from the Opportunities tab.

This reveals essential data on your site, like average position, click-through rate, and impressions. By focusing on the average position column, you can directionally maneuver your internal links.
As shown below, internal links from higher to lower average positions take the scale-down approach. Meanwhile, internal links from higher to fellow highly positioned web pages satisfy the scale-up approach.
3. Facilitated Content Discovery
Aside from guiding users to relevant content, internal links also facilitate the discovery of content for Googlebot. This promotes a deeper topical understanding of your content and an improved grasp of your internal linking structure.
Moreover, stale content tend to have get buried under newly published pages. Internal linking reduces the click depth or number of clicks it takes targeted, especially old content. Helping users find them, breathing life into old content.
Benefits of External Links for SEO
1. Amplified Credibility
External linking to reputable sources lends credibility to your content. This demonstrates thorough research and a commitment to providing valuable external validation to your readers. Plus, external linking supplements your content with additional resources and insights from trustworthy sources, providing a more comprehensive experience for your audience.
There’s just one problem: users have limited control over external links.
In other words, some external links may have ‘decayed’ already, where the web page no longer exists, or the domain has already expired.
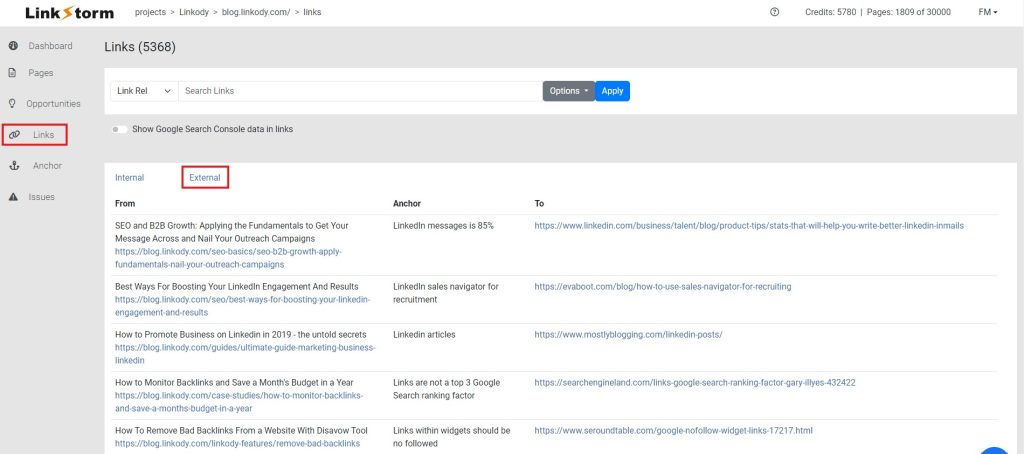
While primarily an internal linking companion, LinkStorm’s Links tab displays all external links throughout your website. This includes the source link, destination, anchor text used, and status so users can know if the link is broken.
2. Improved SEO Performance
While external links don’t directly boost your site’s SEO value, they can still indirectly elevate your SERP ranking. Your willingness to put outbound links signals your trustworthiness in the eyes of web crawlers. This may positively impact your site’s value on Google search results.
3. Networking and Relationship Building
Backlinks are valuable ranking factors for SEO. Outbound linking fosters connections with websites that you’ve linked to. In some cases, they may return the backlink as a token of appreciation. This may even potentially result in collaborative opportunities between the two websites.
Best Practices for Internal Links and External Links
Knowing the differences and respective benefits between internal and external links is one thing. However, understanding the best practices for implementing these links is an entirely different concept.
Below are some actionable tips that you can follow to maximize the effects of your internal and outbound linking efforts:
1. Optimize Anchor Text
Use descriptive and relevant anchor text that accurately reflects the linked content. Anchor texts give users and web crawlers substantial context to understand the hyperlink’s destination.
LinkStorm is a helpful tool for optimizing anchor text. As shown in the example below, the tool’s Anchor tab shows all anchor texts used for internal and external links throughout your website.
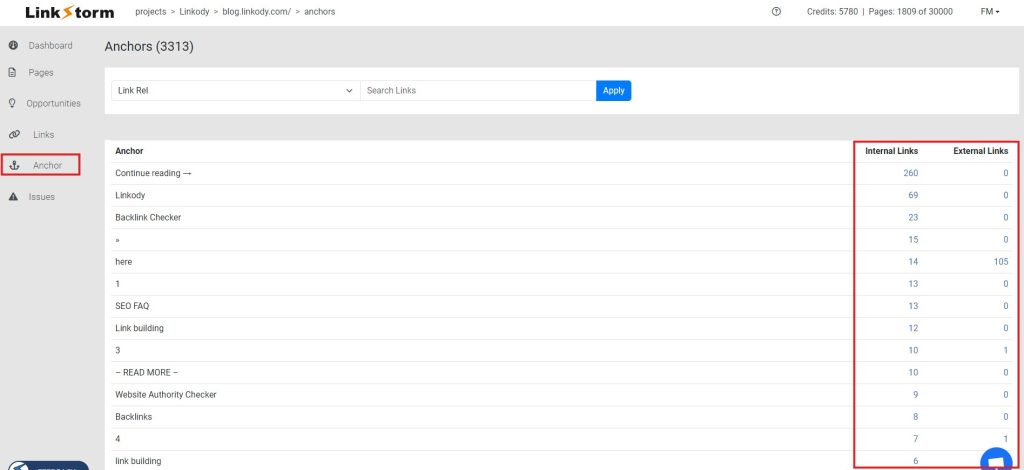
You can then use the information to diversify your anchor text or make your anchors more descriptive.
Related: Best Practices for Optimizing Anchor Texts
2. Qualify Links with the Proper Rel Attribute
Qualifying internal links with nofollow makes no sense because this prohibits link equity from being transferred from the source to the linked page. On the other hand, it’s important to qualify external links with the proper rel attribute to comply with search engine guidelines.
For instance, use rel=”nofollow” if you wish to dis-associate and transfer zero PageRank to the linked page. On the other hand, rel=”sponsored” informs search engines that the outbound link is paid for.
LinkStorm’s Issues tab is a powerful hub for correcting internal linking mistakes, including nofollow links. You can then correct those mistaken attributions via your CMS dashboard.
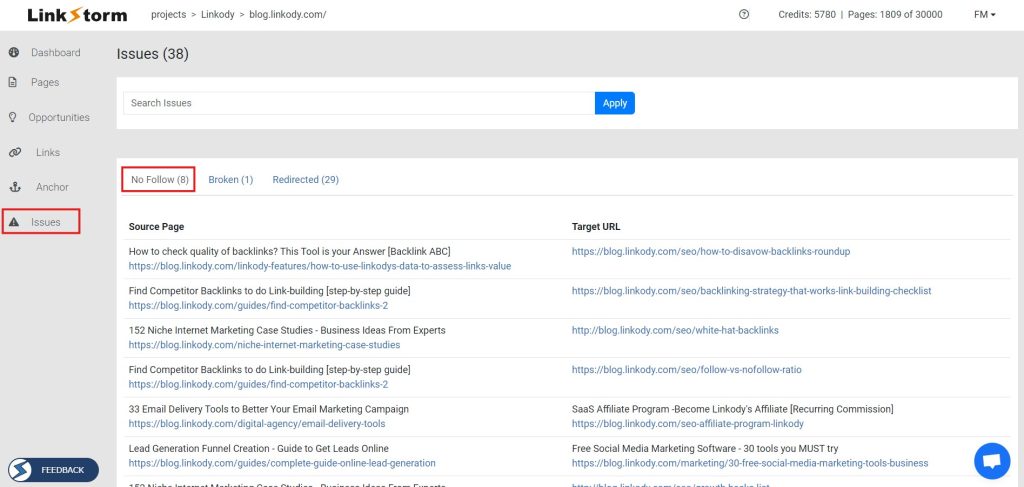
Aside from nofollow links, LinkStorm also reveals broken links and redirects plaguing your website and disrupting your SEO performance. Take advantage of this essential information to get your website up and running as intended.
3. Avoid Link Spamming
Both internal and external links have their merits. However, using them excessively defeats their purpose on your web page. Link spamming refers to the excessive use of links in your content. This creates visual fatigue and information overload in users, especially when encountering a hyperlink-ridden page. As a result, users may then bounce off the page entirely.
Here is an example of a content with excessive links:
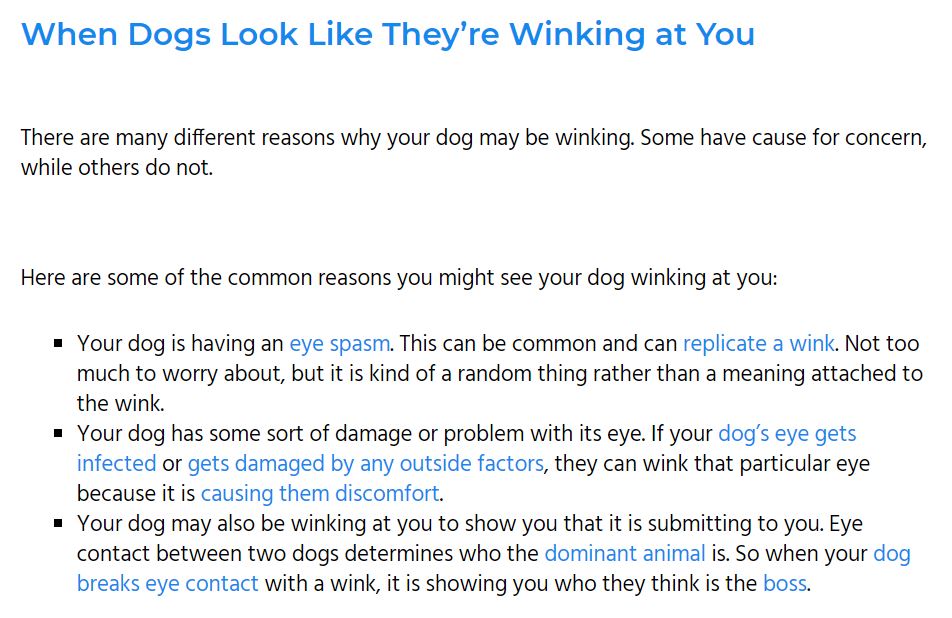
So, how many internal links per page is ideal? It depends. We have a dedicated article that answers this age-old question comprehensively. Check it out.
Other Types of Links You Must Know
Knowing the difference between external and internal links is a precedent that will help set up your link-building campaigns. However, users must also be familiar with other “types of links” for a holistic SEO understanding.
Here are the other types of links all SEOs must be familiar with:
1. Inbound Links
Inbound links, also known as backlinks, are hyperlinks from external domains pointing back to a specific web page on your own website. They are crucial for SEO as they signal to search engines the credibility and authority of your website, potentially improving its search engine rankings.
Backlinks are like the “authority currency” of Google. Having inbound links from authoritative domains is like receiving votes of confidence, which boosts your relevance, trustworthiness, and popularity in your industry or niche.
2. Dofollow Links
Dofollow links are hyperlinks that are not qualified with a rel=”nofollow” or rel=”sponsored” attribute. These links allow search engines to follow them and pass PageRank or link juice from the source to the linked webpage in the process.
These links contribute to the target site’s SEO by telling search engines that the linked content is endorsed or trusted by the source website.
3. Nofollow Links
Unlike dofollow links, nofollow links are hyperlinks qualified with a rel=”nofollow” attribute. As the name suggests, they instruct search engines not to follow the indicated link. The nofollow attribute prevents PageRank from passing from the source to the linked page.
Nofollow links are commonly used to prevent search engines from considering certain links for ranking purposes, like user-generated content, paid advertisements, or untrusted sources. Plus, using nofollow links maintains the integrity of a website’s link profile, ensuring compliance with search engine guidelines on natural linking practices.
4. Sponsored Links
Sponsored links are hyperlinks marked with the rel=”sponsored” attribute, indicating to search engines that the backlinks are paid or sponsored. This was introduced in 2019 when Google revised how the nofollow attribute works.
Google recognizes that the sale of links is embedded in the internet economy. Properly qualifying paid links as sponsored is Google’s way for webmasters to be ‘completely transparent’ with Google. This safeguards them from Google’s penalties if caught violating the search engine’s link spam policy.
5. UGC Links
UGC links, or user-generated content links, are another attribution introduced by Google in 2019. This rel attribute allows webmasters to instruct Googlebot that a hyperlink is user-generated, like a blog comment, and not editorially endorsed by the website.
Like other rel= attributes, UGC links are meant to provide Google with additional information and clarification about the nature of links on your site.
6. Broken Links
Broken links are hyperlinks that no longer lead to the intended destination webpage. When people click those links, they often receive a “404 Not Found” message. Broken links are also one of a website’s most persistent internal linking issues.
Website owners may get broken links for various reasons:
- The linked page is deleted
- The linked page’s URL has changed
- The linked page is moved to a different location
Broken links negatively impact user experience, website credibility, and SEO performance. Regularly monitoring and fixing broken links is essential to maintaining a healthy website.
Need An Internal Linking Ally for Your Website?
Understanding internal links, external links, and all other links is the first step in building a highly proficient and effective link-building strategy. If you want to elevate your internal linking approach, having a robust tool at your disposal can speed up the process.
LinkStorm is an all-around tool that can support your website’s internal linking efforts. With its intuitive interface and powerful features, LinkStorm helps you optimize your internal linking structure, improve user navigation, and boost SEO performance effortlessly.
Say goodbye to broken links, inconsistent anchor texts, and missed linking opportunities. With LinkStorm by your side, you’ll take your website’s linking strategy to the next level.
Explore LinkStorm’s pricing schemes here to find which plan best suits your needs.
Happy linking!
 Written by Joel Cariño
Written by Joel Cariño