A site audit is a necessary SEO activity to ensure that your domain and every page on your site are working correctly. One crucial part of a website audit is verifying the proper implementation of your internal link strategy.
Internal links are essential for websites but are often overlooked in favor of SEO strategies like link building and content marketing. However, a recent study on 23 million internal links revealed an extremely positive correlation between internal links and organic traffic. The study found that sitewide navigational links profoundly contribute to internal linking.
Yes, internal links are essential for websites. But they can also be equally detrimental when not properly managed. This is where an internal linking audit comes in.
This resource dives deep into internal links and how auditing them can impact search engine optimization.
Key Takeaways
- Internal link audits help realize overlooked internal linking opportunities and uncover sitewide issues to help boost a website’s SEO potential.
- Manual internal link audit is only feasible for smaller websites with less than a hundred websites. For large websites, using internal linking tools help with scalability by automating the tedious and lengthy auditing process.
- Internal link audit tools, such as LinkStorm, can automatically find link opportunities and sitewide issues (like broken links, nofollow links, and redirects), which speeds up the site audit process.
- Google Search Console and Google Analytics also provide essential insights to help monitor the impact of internal linking efforts after conducting sitewide audits.
What is an Internal Link Audit?
An internal linking audit is a systematic process of evaluating your website’s internal linking structure to identify areas for improvement and potential issues.
Performing regular audits ensures that your internal links remain effective, relevant, and aligned with your website’s goals.
This, in turn, can enhance the user experience and improve your page authority, resulting in better SERP rankings.
The internal linking audit process typically involves the following steps:
- Crawl your website
- Identify and fix broken links
- Analyze if redirects work as intended
- Qualify your internal links properly
- Diversify anchor text
- Maximize internal linking
- Minimize click depth
- Optimize link placement
- Monitor your internal linking campaign
In the following sections, we’ll explore these steps to help you optimize your internal linking campaign and improve your website’s overall performance.
Importance of Internal Link Audits for SEO
Before we look at the specific steps, let’s evaluate the specific advantages of conducting internal link audits:
Benefit #1: Uncover issues concerning internal links
Some of the most persistent internal linking issues include:
- Broken links
- Redirects
- Nofollow links
- Links with excessive click depth
Conducting an internal link audit uncovers these errors, helping site owners improve their websites. Let’s take a look at each of these internal linking errors below:
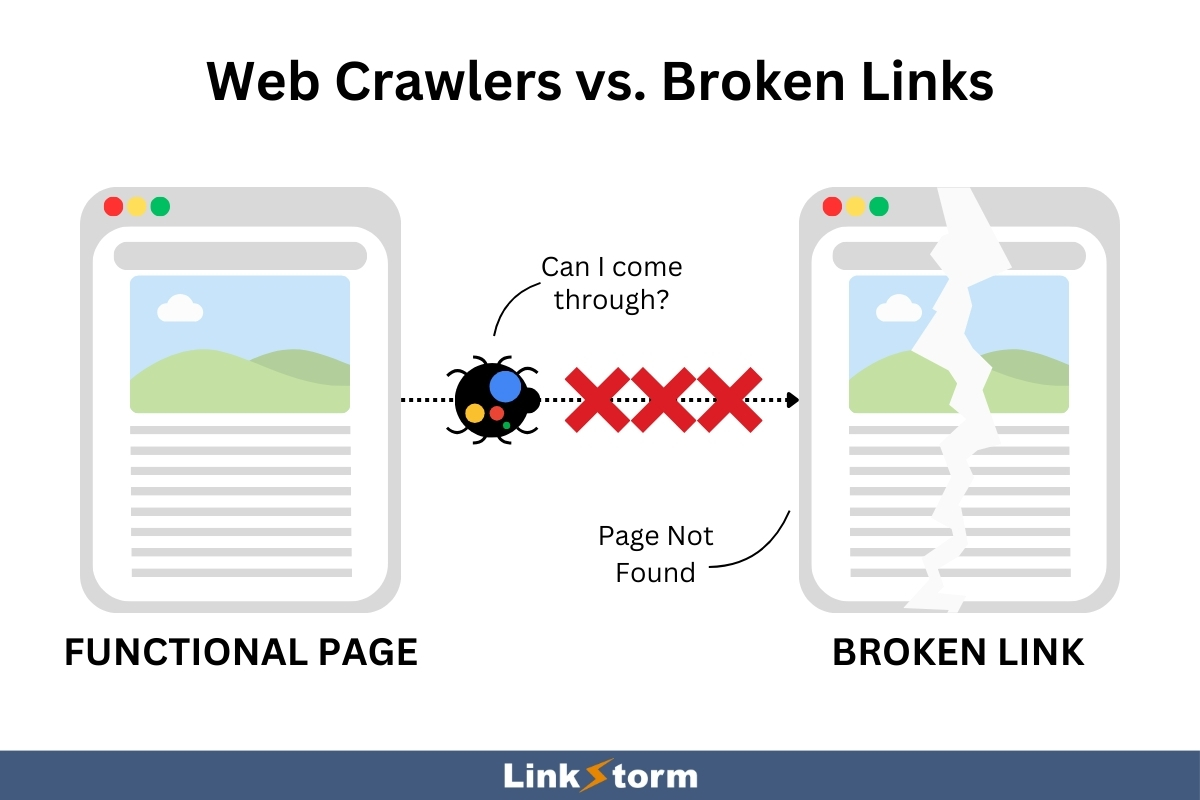
A. Broken Links
Broken internal links are hyperlinks that lead to nonexistent internal pages, which usually take the form of 404 error pages.
They can happen for various reasons, such as page deletion, changes to the target page’s slug, and restructuring your site structure.
Here is what a broken link looks like:
Broken links can lead to poor user experience as it makes your website seem poorly maintained and unprofessional.
Moreover, broken links are dead ends in Googlebot’s crawling journey, causing search engine crawlers to overlook some pages. These links are also signs of poor website management, which might result in SERP ranking dips that bottleneck your site’s visibility and organic traffic.
B. Redirects
URL Redirects are HTML instructions that take users to a different URL than requested. These commands are not inherently bad for a website and may even be beneficial in some cases.
For instance, you are dealing with content cannibalization. Setting up a redirect allows you to transfer the duplicate page’s SEO value to the canonical URL.
Problems only arise when a redirect chain or loop occurs. This happens when a redirect leads to another redirect, which leads to another redirect, and so on.
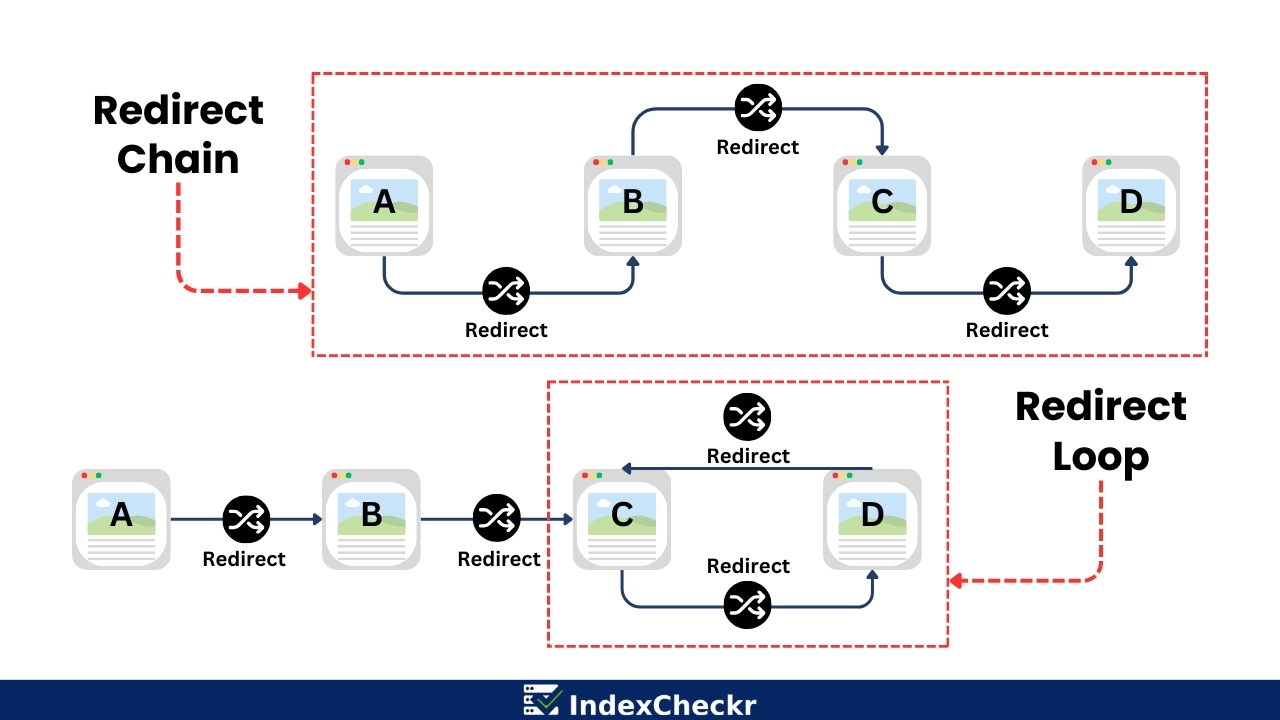
When this happens, site visitors and search engine crawlers cannot reach the destination page, affecting user experience and crawling activity.
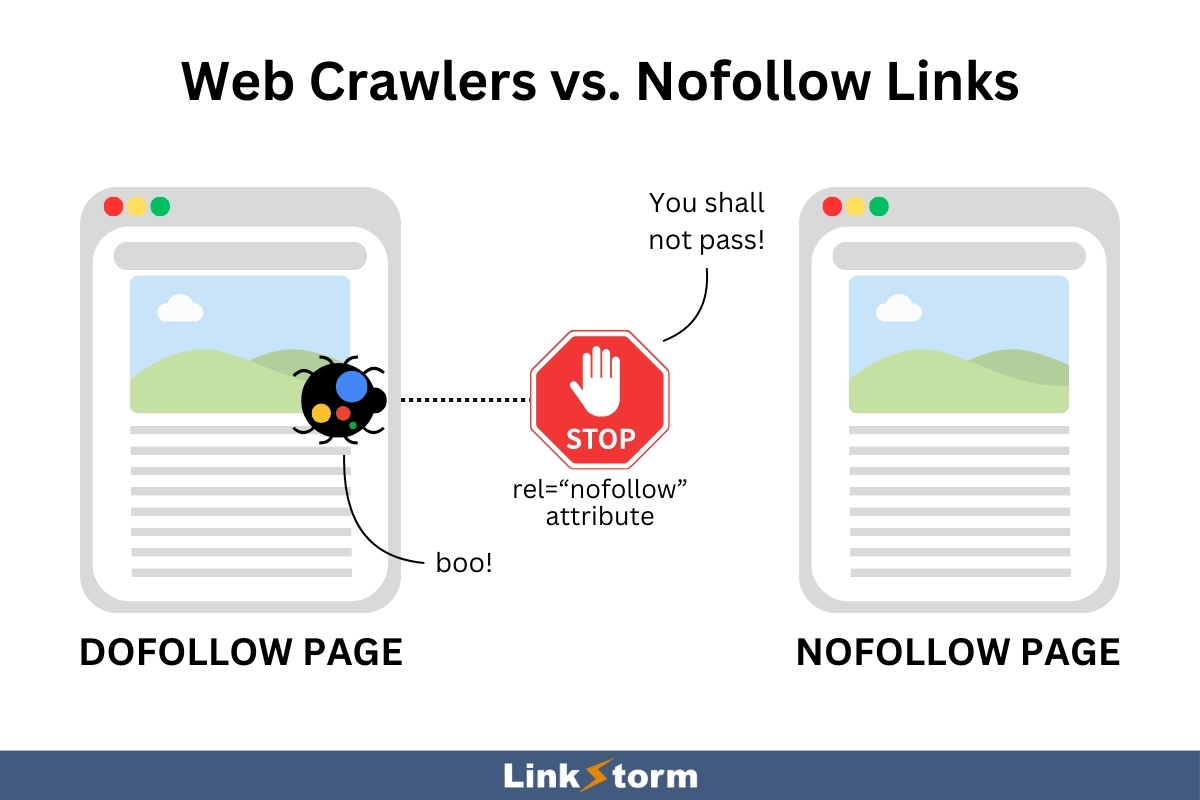
C. Nofollow Links
Internal nofollow links are hyperlinks qualified with a rel=’nofollow’ attribute in the HTML code. This HTML snippet instructs search engines not to crawl the linked page.
The rel=’nofollow’ attribute prevents the transfer of link juice from the linking to the linked page, which limits the SEO growth of targeted pages. When used mistakenly for internal links, you limit the SEO potential of your web pages.
Nofollow links are typically used for external linking, especially when you don’t want to endorse or be affiliated with the external page.
D. Excessive click depth
Click depth refers to the number of clicks required to reach a page from the homepage.
A lower click depth is ideal as it will take users and search engines less time and effort to visit a desired page. This improves SEO by making pages more accessible and enhancing the site’s visibility and user experience.
Conversely, high click depths ruin the user experience by requiring more effort to reach a page.
As more content is published, older content tends to get buried deeply into your site architecture, inevitably increasing the click depth. This causes them to drop in SERP rankings.
Benefit #2: Find internal link opportunities
Webmasters often overlook many internal links throughout their websites. In a recent case study of over 5,000 websites, site owners miss internal links 82% of the time.
Underutilization of internal linking leads to significant content being overlooked, making it harder for users and Googlebot to find. This ultimately negatively impacts the website’s SEO performance and user engagement.
An internal link audit reveals internal link opportunities initially missed during the initial content creation process. Finding internal links manually is a slow and tedious process but doable for smaller websites.
But if you have a large website, there’s more merit in using internal linking tools. These tools can automate finding internal link opportunities, ensuring you maintain a well-connected site.
Benefit #3: Optimize sitewide use of anchor texts
Anchor texts and internal links are directly correlated.
Descriptive anchors make it easier for users and Google to know the context of the linked page. This increases the contextual relevance of the target URL, boosting its SEO value and ranking in search results.
For instance, say you’re linking to a page about “internal link analysis.” Generic anchors like “click here” or “learn more” give zero insight into the linked page, which leaves users and Google wondering what to expect when they click the link.
Optimizing anchor texts allows websites to maximize the impact of internal links for SEO.
Check out the infographic below explaining the different types of anchor texts, plus examples:
Benefit #4: Fix the website’s internal linking structure
Internal linking’s primary goal is to strengthen the connections across pages. A solid internal linking structure is achieved when web pages are effectively interconnected.
This means users can easily reach targeted pages, and Googlebot can efficiently crawl and index pages. However, pages become inaccessible to users and web crawlers when not linked to a site’s main structure. These are called orphan pages, as seen below:
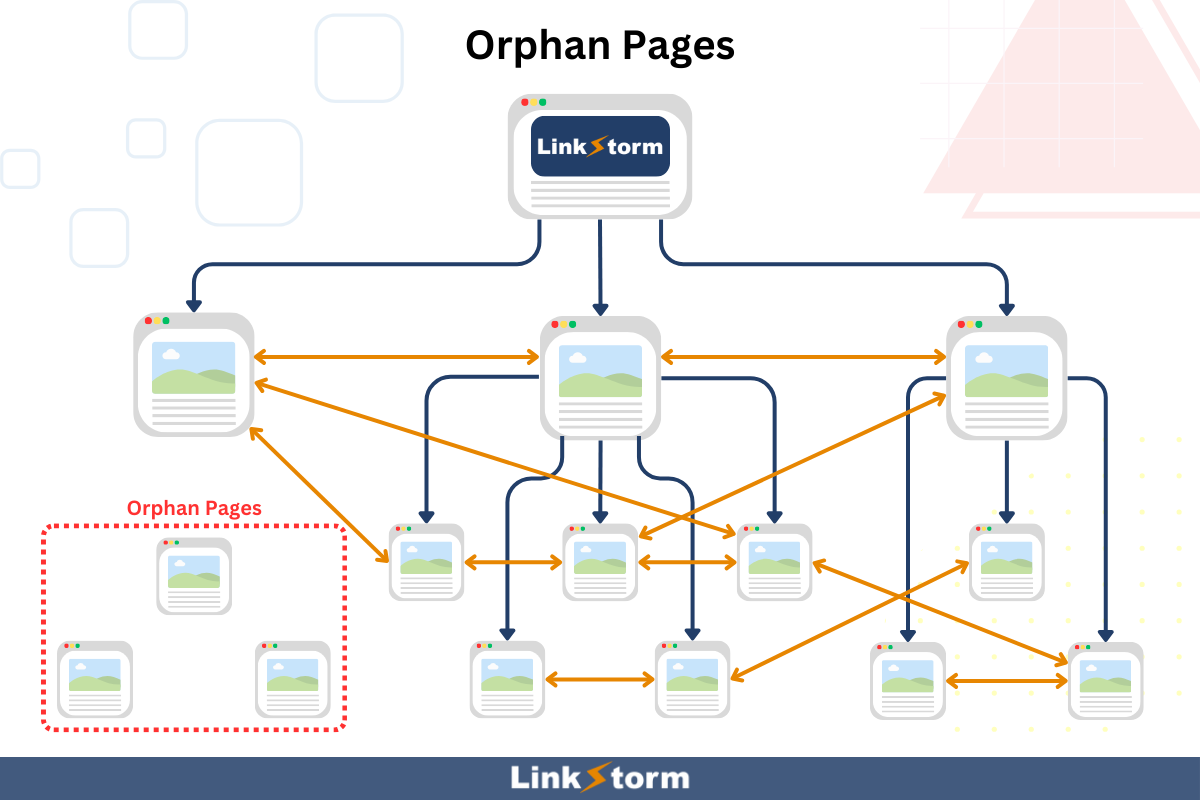
Orphan pages are pages without any internal links pointing to them, making them unreachable from inside your website.
The only way to reach them is:
- Backlinks
- If users know the exact URL
- If the link is included in the sitemap
In other words, this heavily limits orphan pages’ discoverability, crawlability, and indexability.
Auditing internal links lets you find these displaced pages and reconnect them to the website.
Moreover, internal link audits also help site owners restructure and organize content into relevant topical clusters. Topic or content clusters refer to thematically related and interlinked pages composed of a central pillar page surrounded by support pages.

Topical clusters improve SEO by demonstrating topical authority and subject expertise. This signals to Google that your website is a niche authority, giving you leverage to rank better for relevant search queries.
Step-by-step Guide on How to Do Internal Link Audits on Your Website
Step 1: Crawl your website
Crawling involves using a web crawler to systematically scan your website and gather information about its pages and internal links.
This information can then be analyzed to identify issues and areas for improvement in your internal linking campaigns.
LinkStorm has proprietary crawlers that collect essential sitewide data, including URLs, anchor texts, and status codes for each internal link.
For instance, the screenshot below shows all the existing links on LinkStorm’s website, both internal and external links:
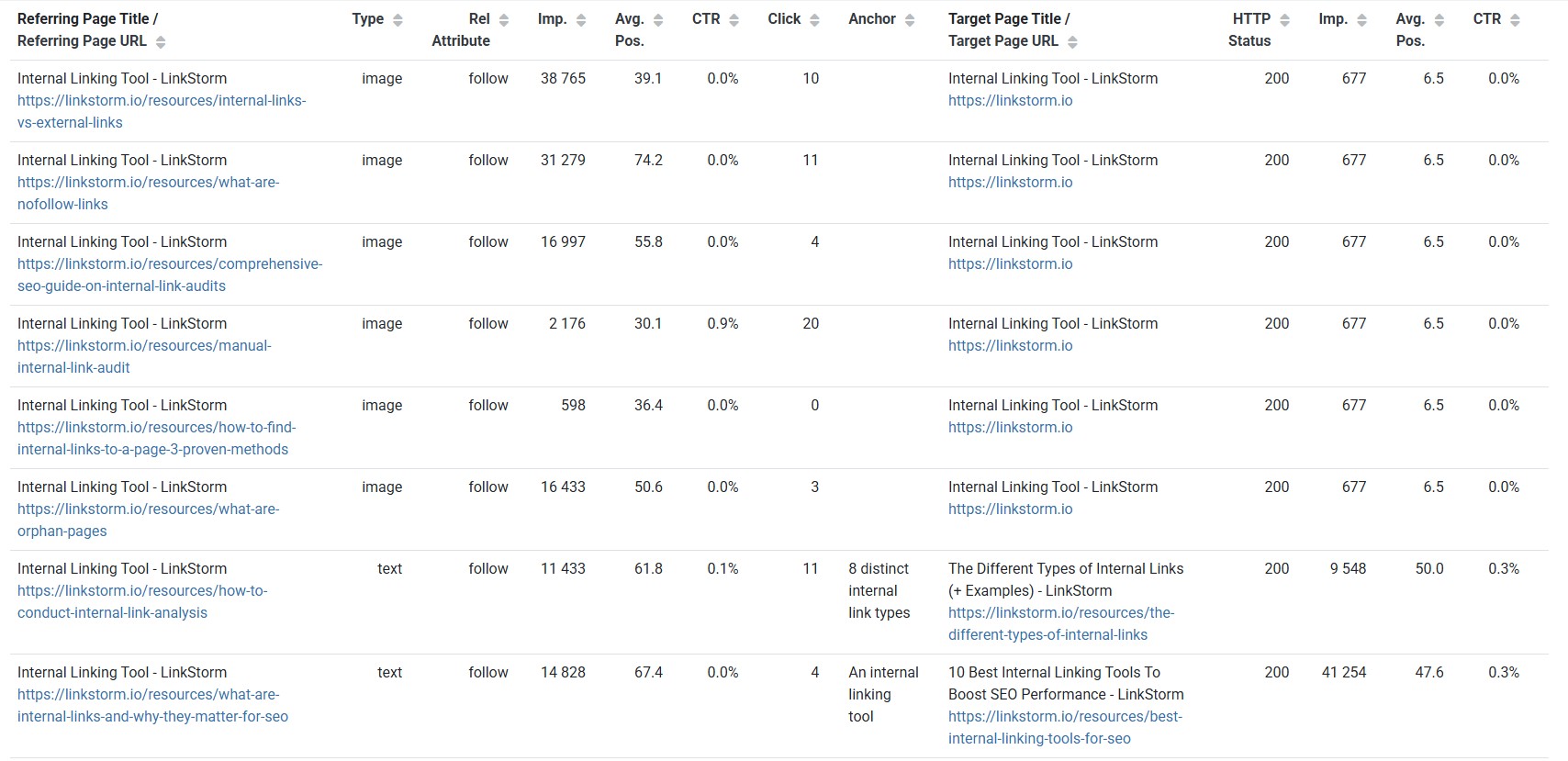
This data becomes the precedent for analyzing internal link issues, anchor text problems, or poor link placement. Site owners can then take corrective measures to rehabilitate those links, improving the effectiveness of their internal links.
To crawl your website, log into LinkStorm and add a new project:
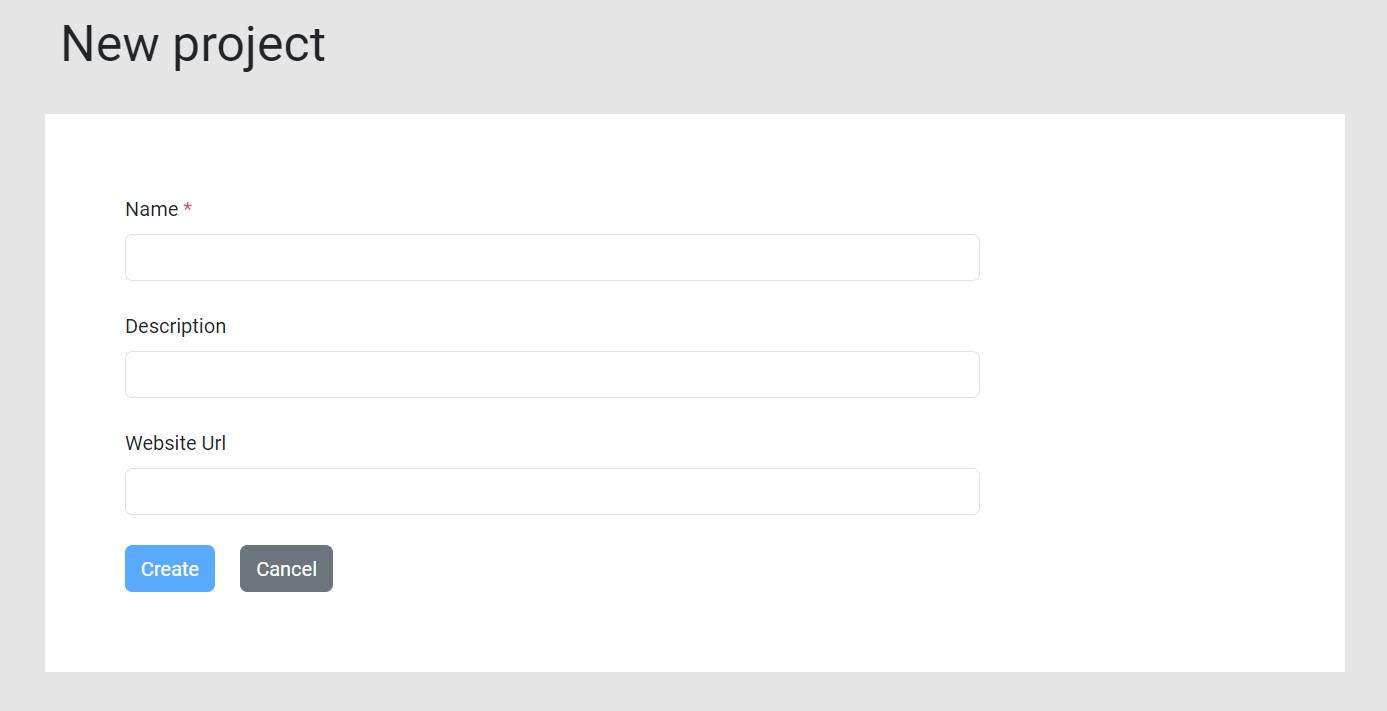
Fill out the necessary information, and LinkStorm will automatically crawl the website.
Here are some of the key data points LinkStorm collects:
- Identify internal linking suggestions
- Unearth internal linking issues
- Reveal all anchor texts used in a website
- List all of the internal and externally linked pages throughout a site
- Show status codes of each link (e.g., 200 for a successful connection, 404 for a broken link, 301 for a permanent redirect)
Step 2: Identify and fix broken links
Broken links are persistent internal linking issues on a website.
LinkStorm helps you address them by scanning your website for any broken links.
From the tool’s dashboard, select the Issues tab on the sidebar menu.
Click the “Broken” option from the Issues tab interface to show the broken links on the website.
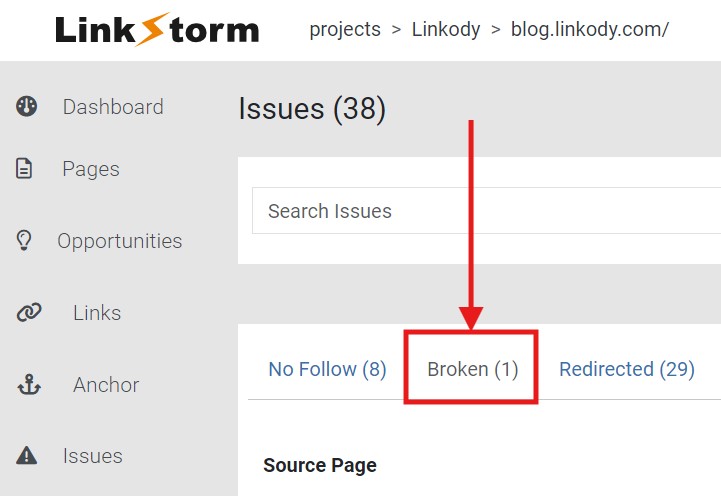
In this example, we used Linkody’s website as a reference. As shown below, they only have one case of a broken link on their domain.
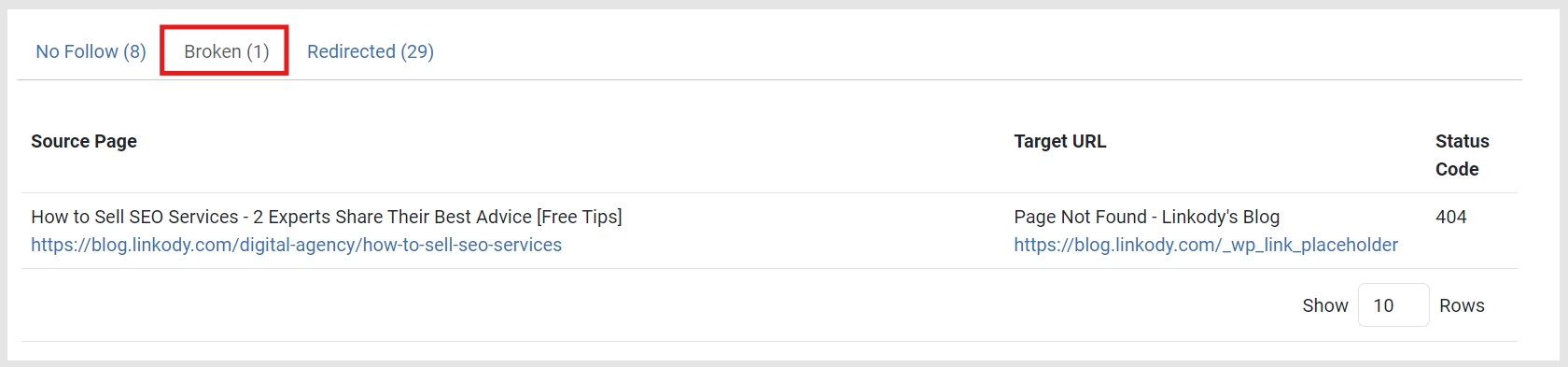
The Source Page column indicates the page where the broken hyperlink is located. The Target URL column shows the broken destination itself.
You will also find the HTTP Status Code, which is usually 404 most of the time for ‘Page Not Found.’
However, a 503 error or ‘Service Unavailable’ may occasionally appear when the service is overloaded and cannot process the request.
After discovering the broken links, return to your CMS to resolve the errors either by:
- Updating the target URL with the correct link
- Replacing the broken link with an alternative URL
- Removing the link altogether
Step 3: Analyze if redirects work as intended
If you’re already on the Issues dashboard, simply jump tabs from the “Broken” to the “Redirected” option.
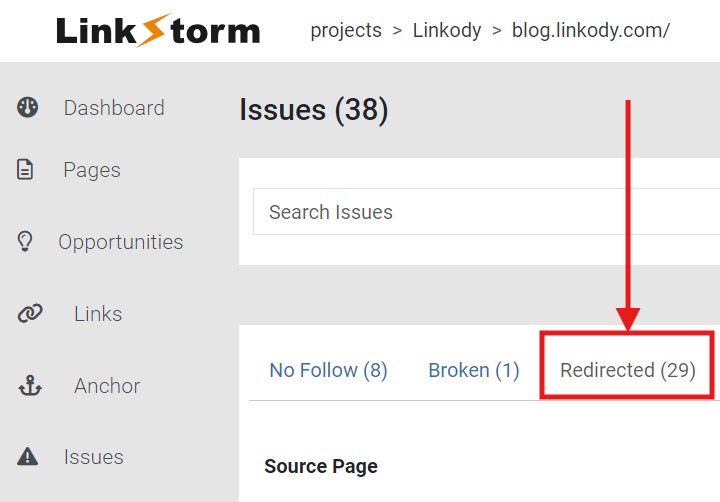
This shows all the redirected pages on your website and other essential data concerning redirects, such as the Source Page, Target URL, Status Code, and Target Final URL.
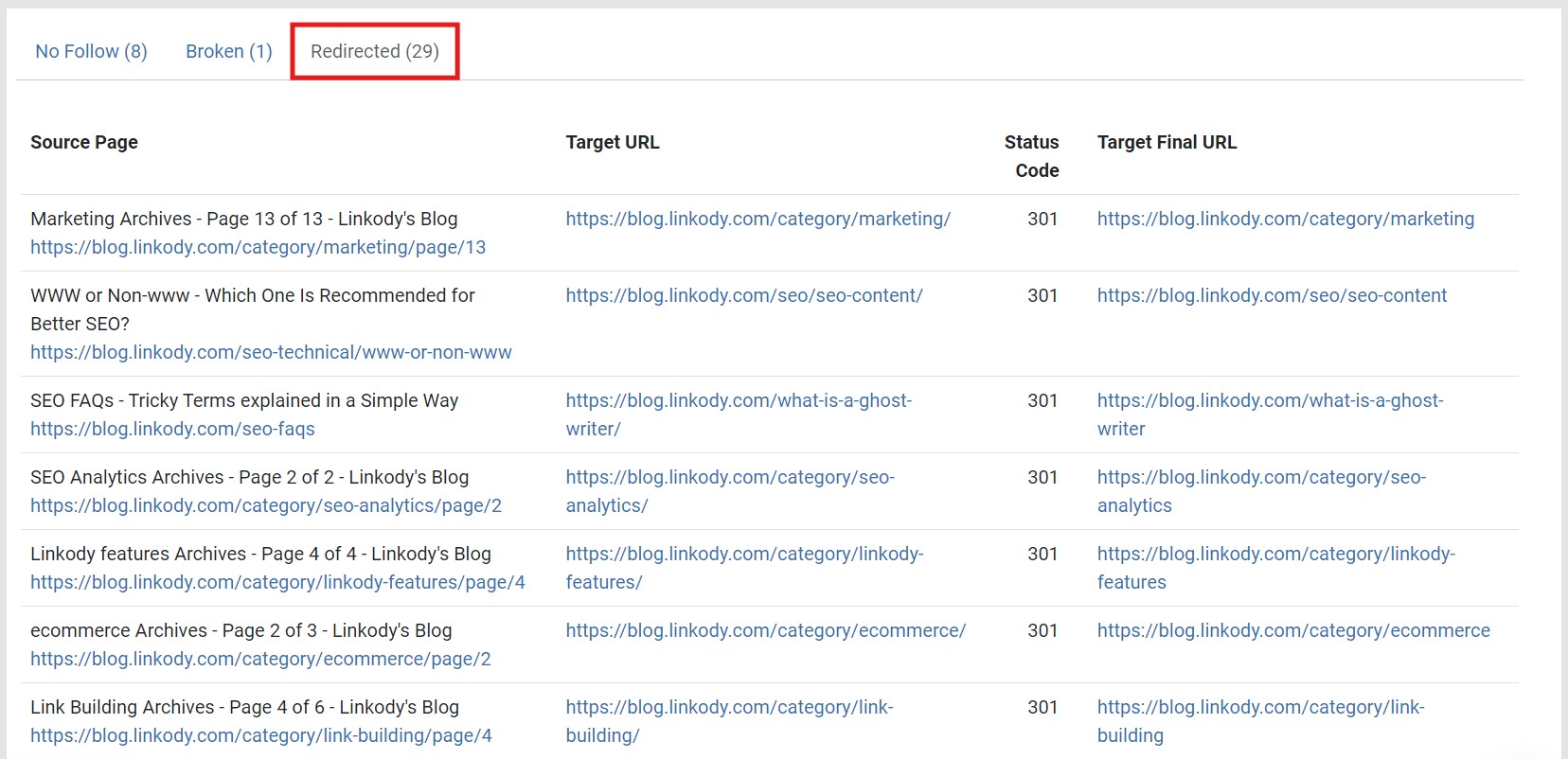
As the above example shows, most redirects are 301, meaning permanently redirected. That means users will be taken to the link on the Target Final URL when they click the original Target URL.
Some redirects are good, but mismanaged redirects can result in redirect chains or loops.
To test if you’re dealing with a redirect loop, click one of the Target URLs listed on the tool. Pages in redirect loops often buffer continuously until an error message pops up, just like this one:
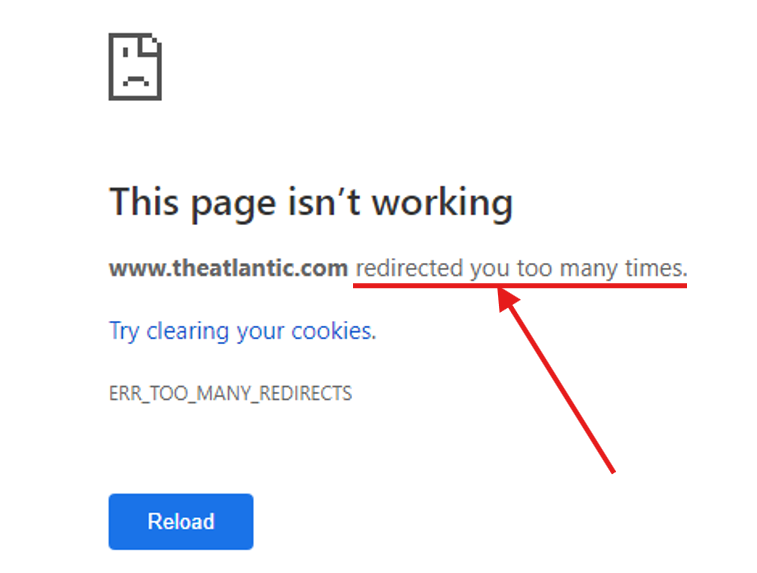
Redirect loops always end on the same link it began with. Once you find a page in a redirect loop, copy the page’s Target URL and Target Final URL on the search bar and click Apply, as shown below.
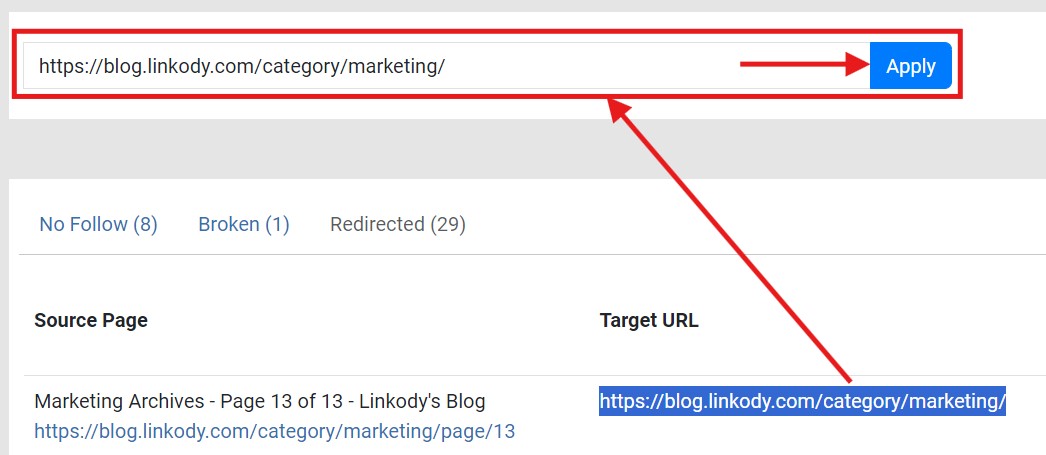
Typically, this should only show ONE redirect command involving those URLs. If more than one redirect is shown, it could mean the pasted link is involved in a redirect loop or chain.
Repeat this process until you find all the pages in the redirection error.
Step 4: Qualify your internal links properly
From LinkStorm’s Issues tab, click the No Follow option.
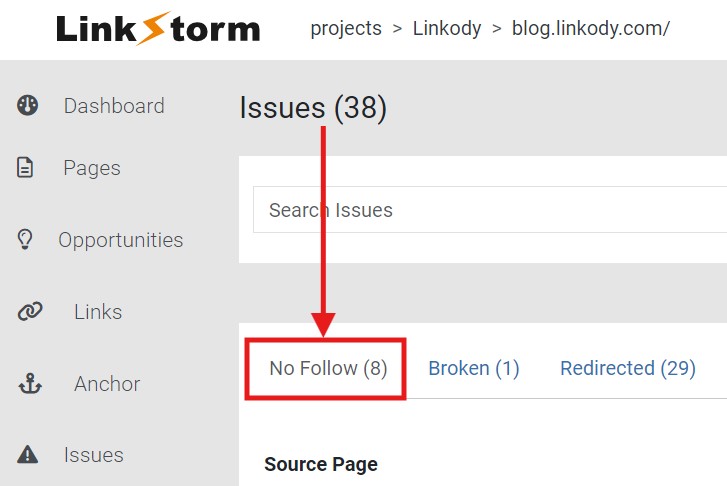
This will show all of the internal links qualified with a rel=’nofollow’ attribute.
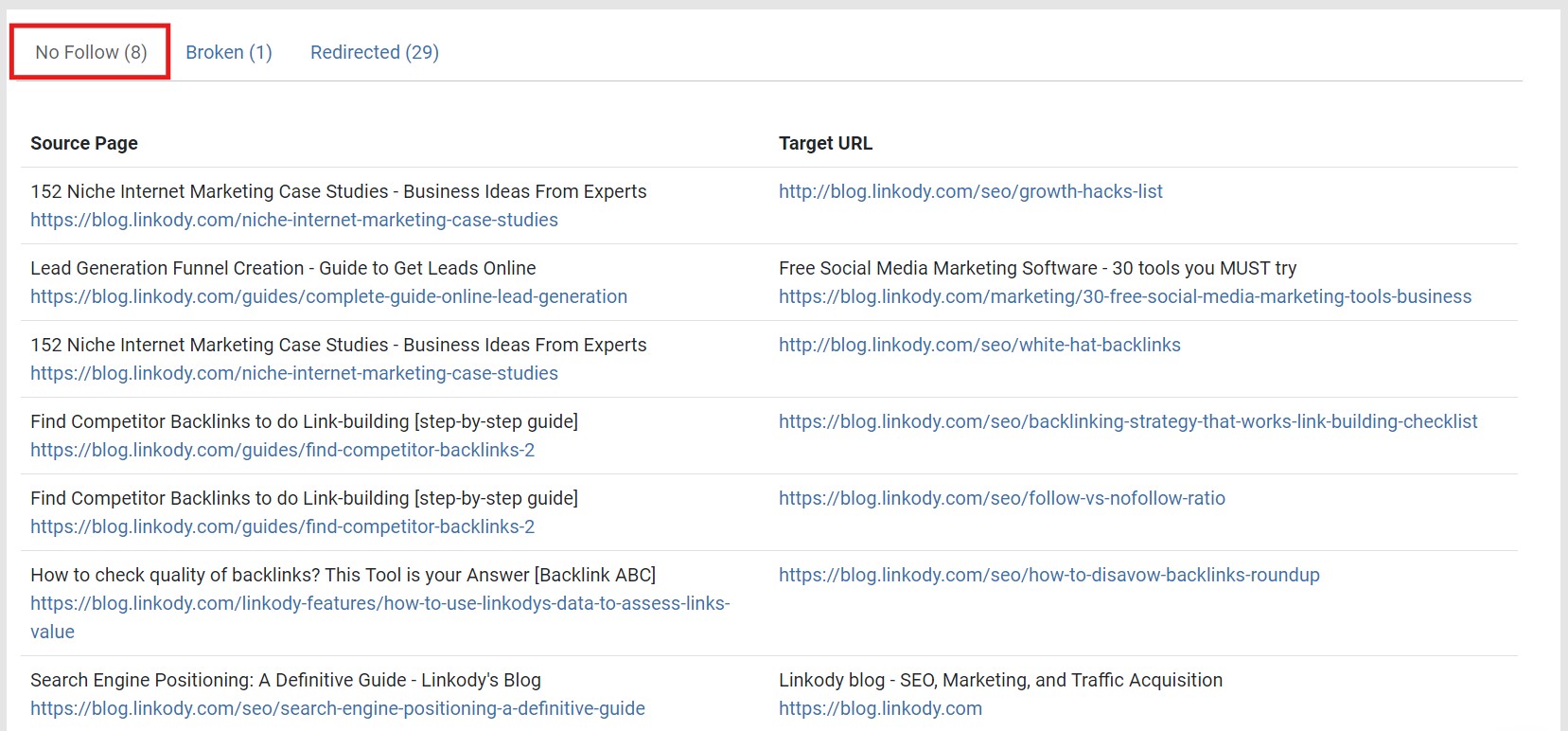
Ideally, all internal links must be dofollow to allow Googlebot to crawl the website easily and distribute link equity.
Unlike redirects and broken links, fixing nofollow links is easier.
Many CMS, like WordPress, are equipped with tools and plugins that allow users to toggle a button to set a link as nofollow or sponsored. Below is an example:
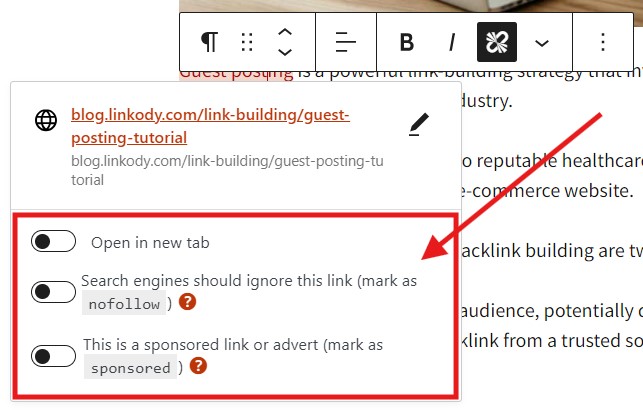
This removes the hassle of manually checking the links’ HTML source code and removing unwanted rel attributes.
Step 5: Diversify anchor text
Anchor text plays a crucial role in conveying the context of the linked content to both users and search engines.
Descriptive and relevant anchor text can help users quickly understand what to expect when clicking a link while allowing search engines to comprehend the relevance between pages better.
LinkStorm gives users a bird’s eye view of their website’s anchor texts. To do this, select the Anchor tab from LinkStorm’s sidebar menu.
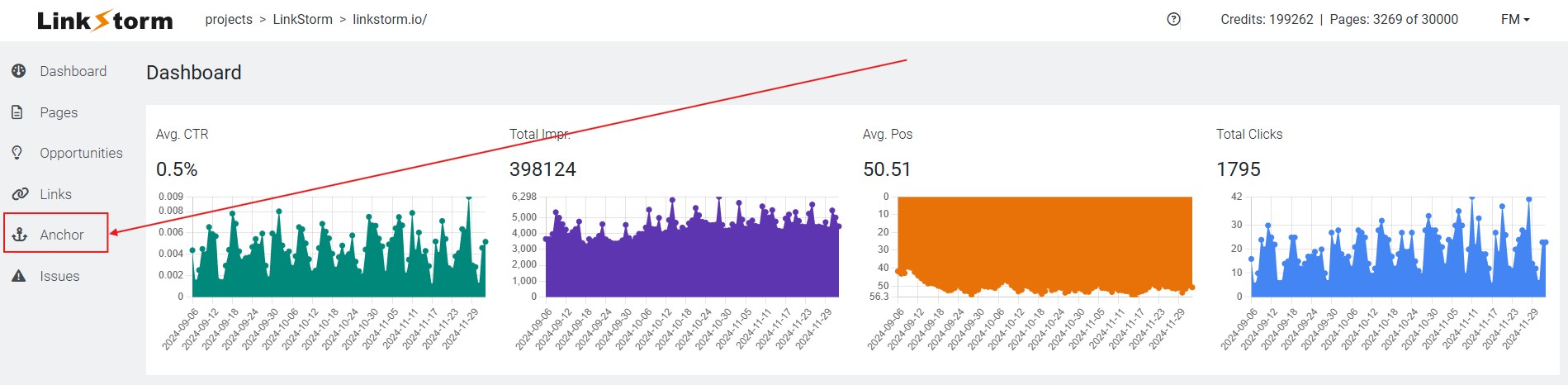
This will show all the anchor texts used on your website, including how many times they were used and the destination of those anchors, whether internal or external links, as shown below:
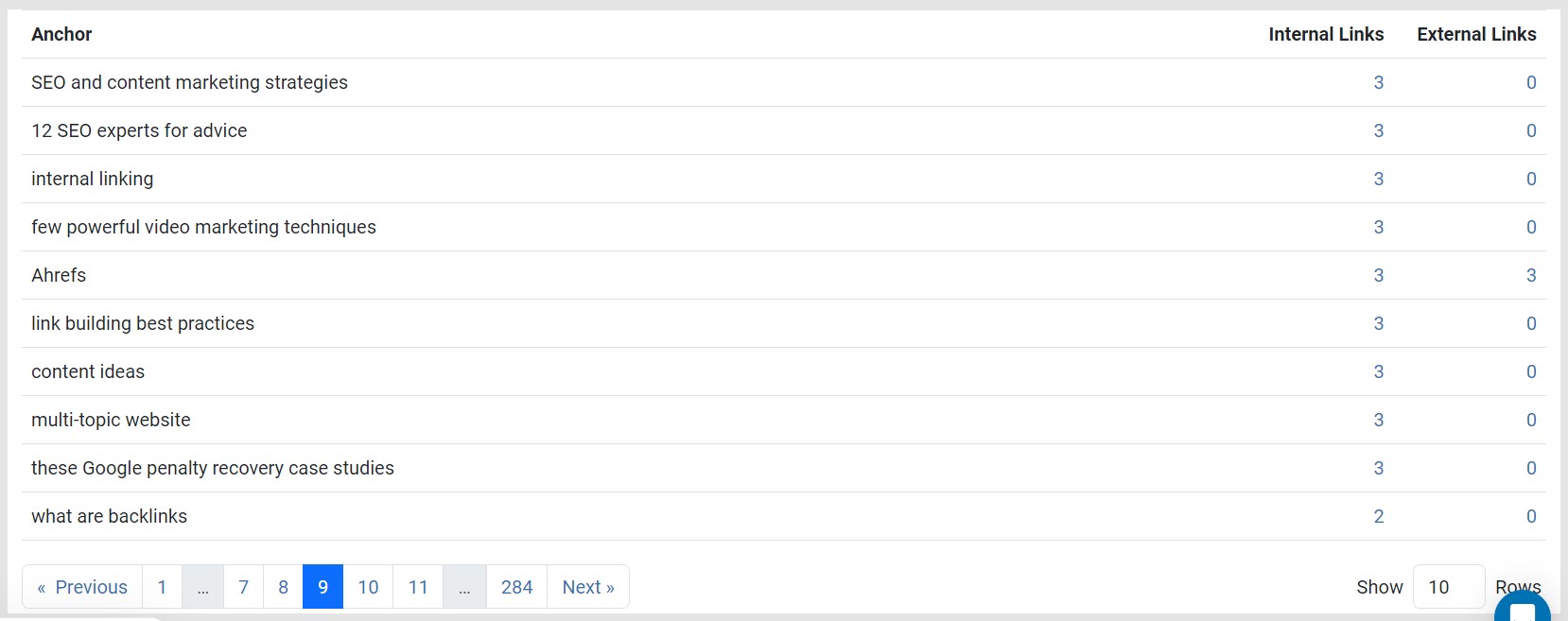
Clicking any number under the Internal or External column will list the links where the particular anchor text was used.
For example, the anchor “SEO and content marketing strategies” are used 3 times on the following links:
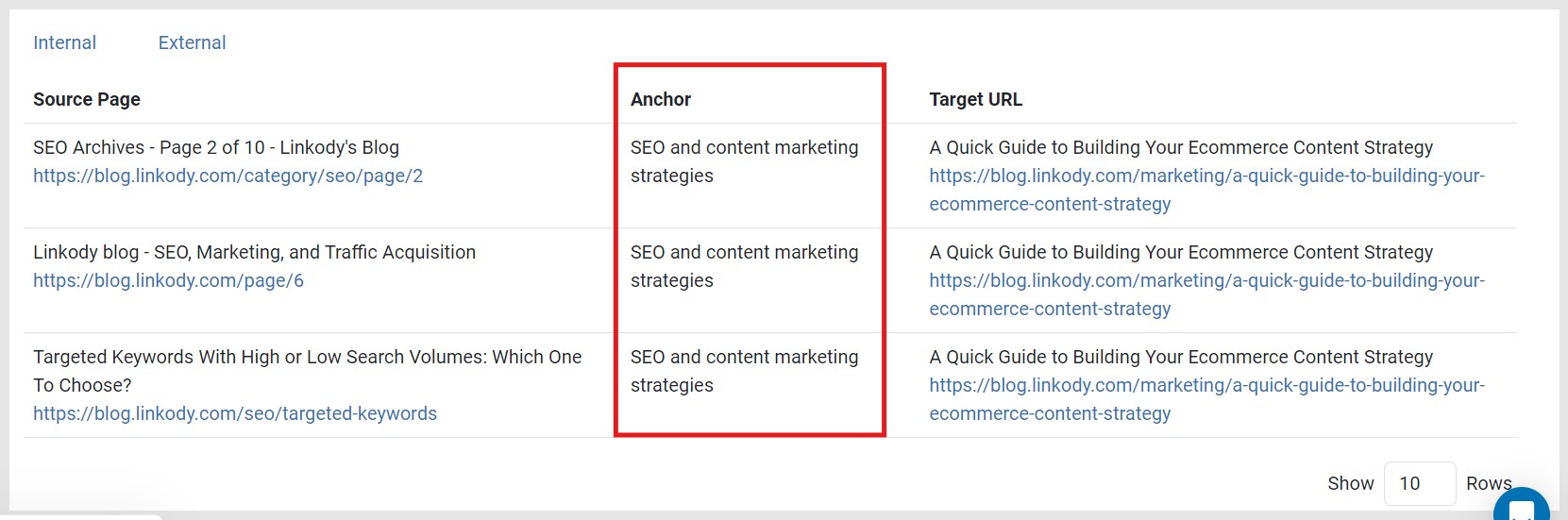
LinkStorm’s Anchor tab is essential for diversifying anchor text usage throughout a website. If several links on your site use exact-match anchor texts, Google might flag those links as spammy. This puts you at risk of suffering SEO-damaging penalties from the search engine.
On the other hand, the Anchor tab is also helpful for avoiding anchor text over-optimization. Avoid stuffing anchors with keywords, and ensure they read naturally.
It’s advisable to use a variety of anchor texts, such as exact-match, partial-match, and phrase-match anchor texts.
Here are some quick guidelines for effective anchor text usage (descriptive, relevant, concise):
- Make it descriptive. Clearly communicate the topic or purpose of the linked page
- Ensure relevance. Use keywords that directly relate to the content of the target page
- Keep it concise. Use short, clear phrases that accurately represent the linked content without being overly lengthy
With Linkstorm’s analytics and insights, you can monitor the effectiveness of your anchor text, helping you refine your internal linking strategy and improve your website’s performance.
Step 6: Maximize internal linking
Many internal link opportunities get lost under the radar during the content creation process. These missed link opportunities are sometimes revealed only during an internal linking audit.
Maximizing sitewide internal linking strengthens your site structure, ensuring users do not miss any relevant pages during navigation and Googlebot does not overlook any pages when it crawls the website.
LinkStorm assists site owners in maintaining a well-connected website by providing a list of internal link suggestions.
To do this, click the Opportunities tab from the LinkStorm dashboard.
This takes you to a page where you can select between LinkStorm’s algorithms for finding internal link opportunities: Semantic Similarity and Content Matching.
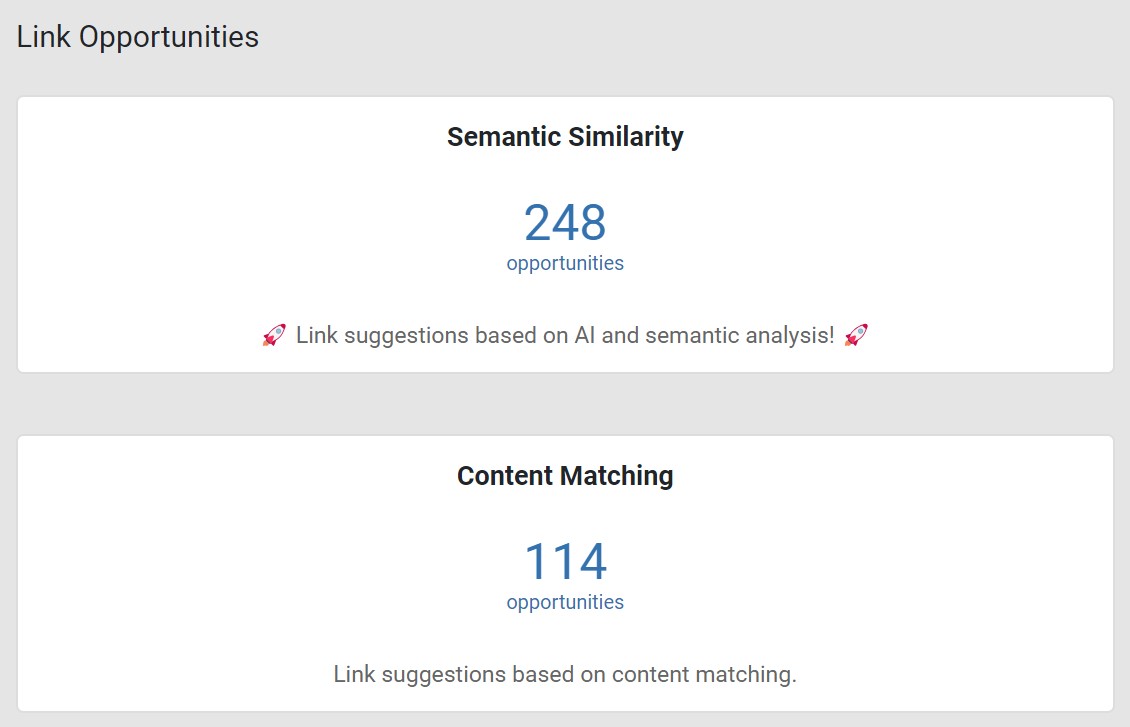
Here’s how each works:
- Semantic Similarity: LinkStorm’s AI uses semantic analysis to understand the content of a page and find contextually relevant pages to link.
- Content Matching: LinkStorm searches seed keywords throughout the website as anchor text placeholders for internal link placement.
Either algorithm will list link opportunities and other essential information, such as the Source Page, Suggested Placement, and Target Page, as shown below:
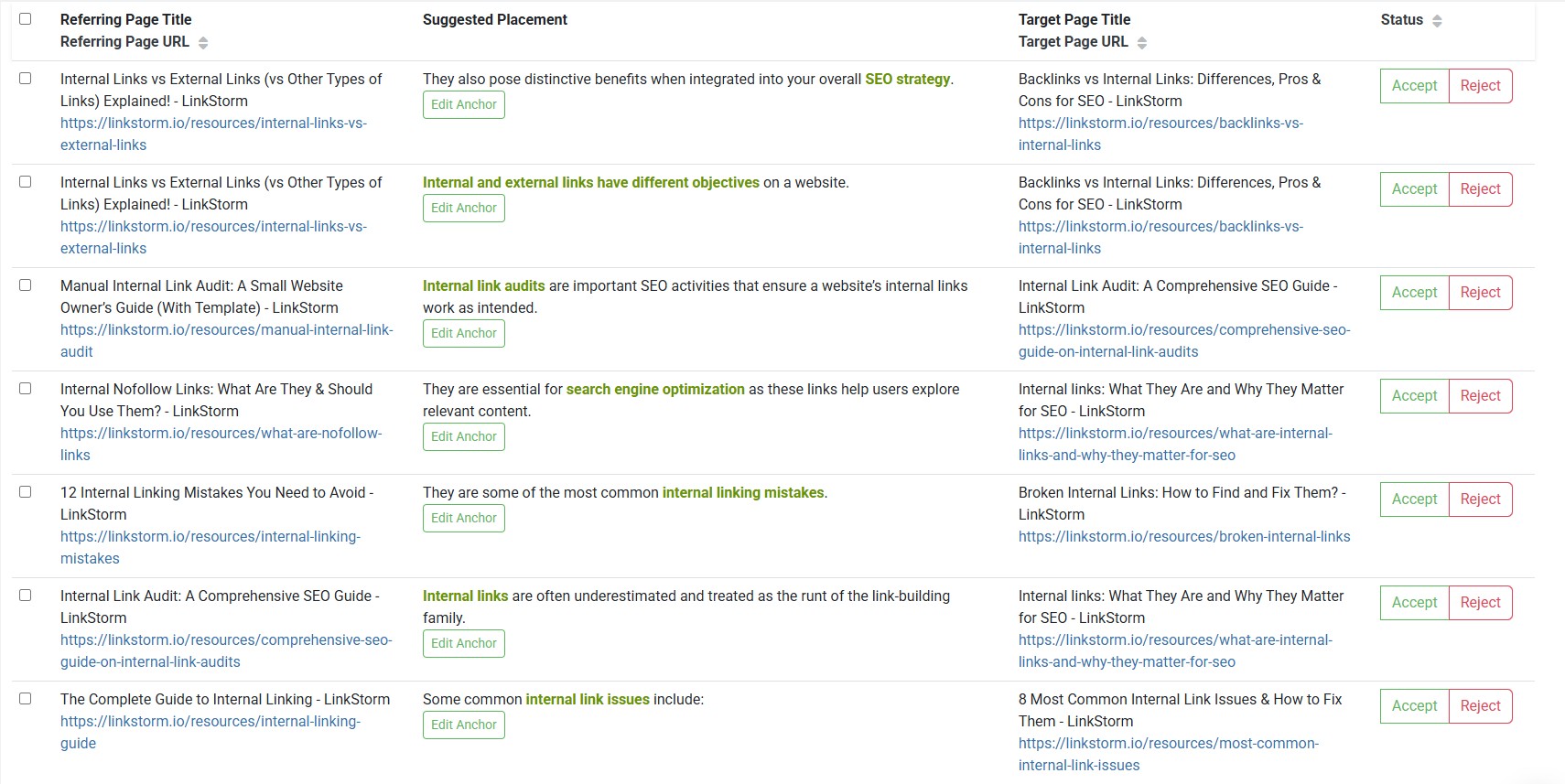
If preferred, you may select a new anchor text. You can also configure the table to add additional columns like relevance score, click depth, and GSC metrics.
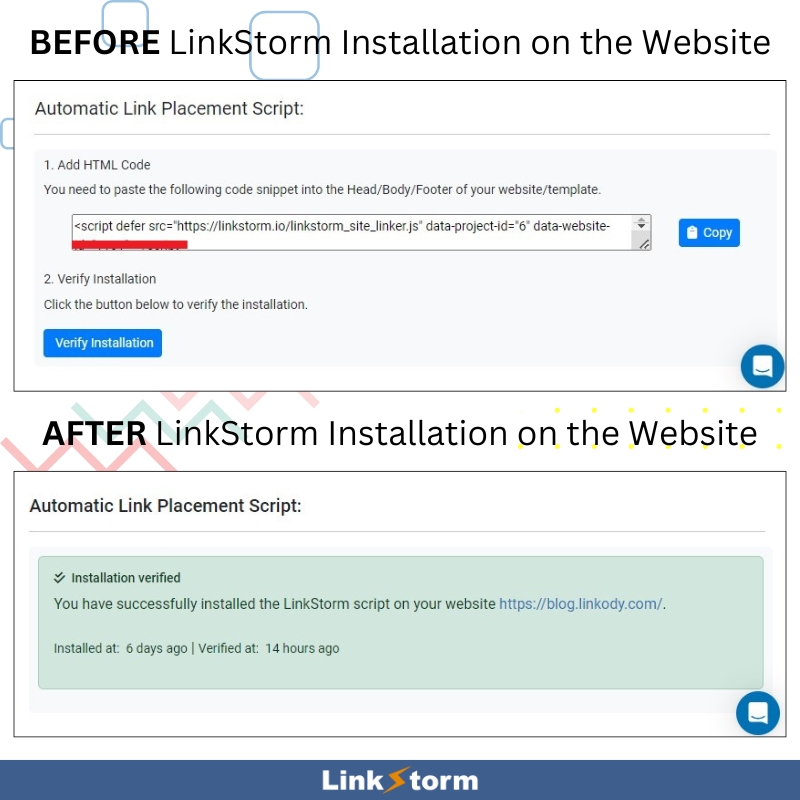
Once you’ve installed LinkStorm on your website, accepting a link suggestion happens seamlessly. Every link you accept gets embedded in your content in real-time.
To install LinkStorm’s snippet of code on a website, visit the main dashboard. At the bottom right, you will find the HTML snippet you must paste on the website’s Head, Body, or Footer.
Step 7: Minimize click depth
The click depth of older pages or stale content increases as more pages get published on a website.
LinkStorm’s Opportunities tab lets site owners optimize click depth by connecting contextually relevant stale and new content.
For instance, consider the internal link suggestions below:
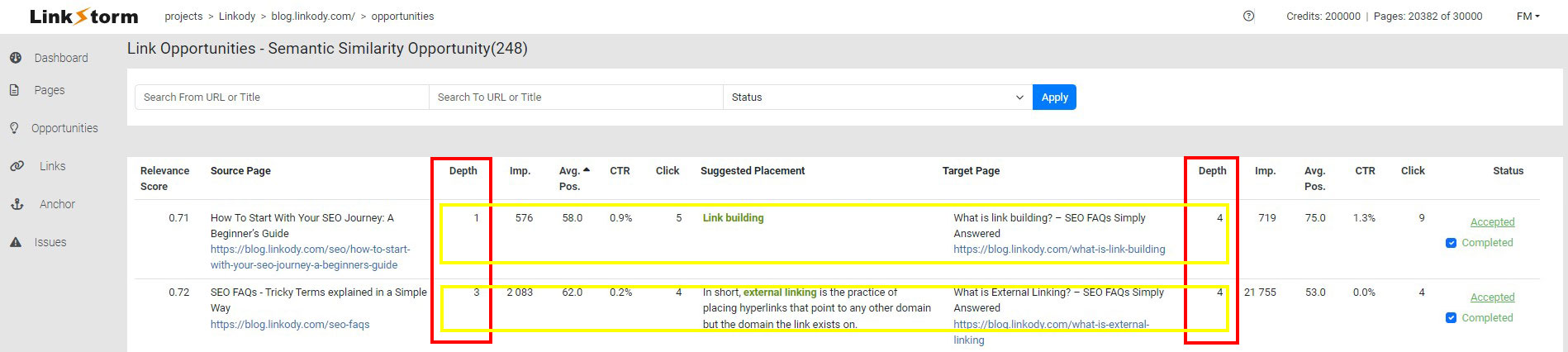
By connecting low-click depth with high-click depth pages, you consciously reduce the number of clicks it takes to reach the target page.
In the example above, connecting a page with a click depth of 1 to another page with a click depth of 4 will reduce the latter’s click depth to 2. This breathes new life into the old content.
Google will notice if fresh traffic enters the old page, which may result in improved SERP ranking or search performance.
Another way to optimize click depth is linking important or high-conversion pages from the homepage or main navigation menu. The closer a page is to the homepage, the more important it seems in Google’s eyes.
Step 8: Optimize link placement
The placement of internal links within your website can impact user experience and SEO.
Strategically positioned links can guide users through your site, encouraging them to explore further and increasing engagement.
One strategy to optimize link placement is positioning links in high-visibility areas. For example, place important internal links where users will likely notice them, like the main content, navigation menus, or sidebars.
Another technique is to avoid excessive internal linking. Too many internal links can make the content appear spammy to search engines and challenging to read for users.
For instance, take a look at the screenshot below:
Spamming content with links may cause visual fatigue or information overload. In some cases, users may bounce off the page immediately since the internal links feel like they are shoved down users’ throats.
Third, use contextual links to add value and relevance. Whenever possible, include contextual internal links within your content to allow users to explore related content in their search journey.
Step 9: Monitor your internal linking campaign
As your website grows and evolves, it’s crucial to perform regular internal linking audits to maintain the effectiveness of your internal linking strategy.
Regular audits help you identify new opportunities for improvement, detect new issues, and ensure your website remains aligned with your objectives.
Here are additional tips for updating and refining your internal linking strategy based on performance data:
- Analyze user engagement metrics, such as bounce rate, time on page, and click-through rate, to identify underperforming pages
- Monitor search engine rankings to understand the impact of your internal linking efforts on your website’s visibility
- Experiment with different link placements, anchor texts, and various types of links to determine the most effective combinations for your audience
Linkstorm’s comprehensive suite of features makes managing your internal links easier, ensuring they support your website’s SEO performance.
Best Tools to Aid LinkStorm in Auditing Internal Links
LinkStorm is a specialized, all-in-one internal linking toolkit designed to help owners manage their internal linking activities.
While revolutionary in its use of artificial intelligence, there are additional tools you can use to support LinkStorm’s site auditing capability.
Below, we’ll look at some tools to help audit your internal links and overall SEO strategy:
Google Search Console
Google Search Console provides invaluable data to help optimize internal linking efforts.
For one, the indexing tab shows which pages are not being crawled or indexed, hindering internal link effectiveness. The performance report also reveals which pages drive traffic and which are underperforming, which you can use to prioritize internal linking efforts.
Site owners may also use GSC to analyze the impact of the internal linking campaign on the SERP performance of pages.
Google Analytics
Google Analytics is another Google-offered tool that offers valuable insights for optimizing internal linking strategies.
For instance, pages with high bounce rates or low engagement may suggest weak internal linking. You may also use GA to analyze popular content and link to high-conversion pages to maximize business value.
Finally, GA can help you understand how users move through your website. Identify bottlenecks and areas where internal links can improve user experience and encourage deeper exploration.
Can I Audit My Internal Links Manually?
It is possible to audit internal links manually, especially if you’re dealing with a relatively small website or less than 100 web pages.
However, this process will take time and effort. The audit process might also take several days or weeks to complete.
Performing a manual internal linking audit does not require paid tools or subscriptions to SEO software. It can be accomplished using only free and complementary website management tools like Google Search Console and Google Analytics.
Here is an overview of the general steps to follow:
- Create a database of all your content by listing your web pages on a sheet. Insert essential details by adding the following columns to the database: Page Title, URL, Category, Publication Date, and Excerpt.
- Arrange your pages into pertinent topical clusters based on the Page Title, Category, and Excerpt.
- Starting with one topical cluster, manually visit each page and find viable anchor text placeholders for internal linking with other pages within that cluster. If there is no room for internal link placement, modify the copy to create space for internal links. The goal is to have all pages within a cluster interlink with each other to establish topical authority on the subject.
- Once every topical cluster is effectively interlinked, you will have dedicated information hubs or a collection of inter-related content for specific topics. The next step is finding an opportunity to connect each cluster with others on similar topics.
Doing the above steps ensures your website is well-linked, making up for a successful internal linking strategy.
Manually auditing websites is doable, provided you have time, patience, and the benefit of a small website. However, using SEO tools to audit internal links is ideal for larger websites housing hundreds of pages.
Audit Your Internal Links with LinkStorm
Internal links are often underestimated and treated as the runt of the link-building family. However, when used strategically, they can have a massive impact on your site’s SEO and search engine rankings.
An internal link audit bridges the gap between your website’s current SEO performance and its potential for SEO improvement. LinkStorm is the all-in-one internal linking auditing tool that can take your website where it needs to be.
Try LinkStorm’s now for FREE—no credit card requirement, no strings attached.
Happy linking!
 Written by Joel Cariño
Written by Joel Cariño